| Reading and Concatenating SAS Data Sets |
| Merging vs.
Concatenating |
| Now that you've learned how to create a new data set by
reading a single existing data set, you may want to combine two or more data
sets. There are two basic ways to combine data sets:
concatenating and merging.
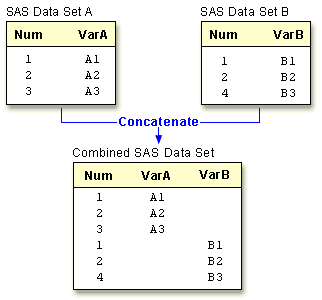
In concatenating, data sets in the SET statement are read sequentially, in the order in which they are listed, until all observations have been processed. The new data set contains all the variables from all the input data sets and the total number of records from all input data sets. data concatenated;
set a b;
run;
|
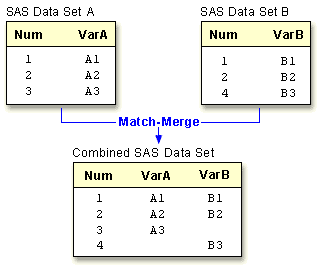
Most merges are combined with a BY statement to produce
a match-merge of two or more data sets. When a BY statement
is used, observations are match-merged according to the values of the BY
variable(s). You can see from the graphic below how the results of a
match-merge differ from the results of a concatenation of data sets (in this
case the BY variable is Num).
data merged;
merge a b;
by num;
run;
|
| The rest of this lesson discusses concatenating. To learn more about merging, refer to the lesson Merging SAS Data Sets. |
  |
|
Copyright © 2002 SAS Institute Inc.,
Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.