| Quiz:
Reading
Hierarchical Files
Select the best answer for each question and click Score My Quiz.
-
Which of the following is true
for the RETAIN statement?
-
Which SAS statement reads the value
for
code (in the first field), and then holds the value
until an INPUT statement reads the remaining value in each observation
in the same iteration of the DATA step?
| 1---+----10---+----20---+----30 |
| 01 Office Supplies |
| 02 Paper Clips |
| 02 Tape |
| 01 Art Supplies |
| 02 Crayons |
| 02 Finger Paint |
| 02 Construction Paper |
-
Which SAS statement checks for
the condition that
Record equals C and executes
a single statement to read the values for Amount?
-
As the DATA step begins the sixth
iteration, which illustration of the program data vector is correct?
| 1---+----10---+----20---+----30 |
| H Lettuce |
| P Green Leaf Quality Growers |
| P Iceberg Pleasant Farm |
| P Romaine Quality Growers |
| H Squash |
| P Yellow Tasty Acres |
| P Zucchini Pleasant Farm |
data perm.suppliers (drop=code);
infile orders;
retain Vegetable;
input code $1. @;
if code='H' then input @3 Vegetable $6.;
if code='P';
input @3 Variety : $10. @15 Supplier : $15.;
run;
proc print data=perm.suppliers;
run;
-
What happens when the fourth iteration
of the DATA step is complete?
| 1---+----10---+----20---+----30 |
| F Apples |
| V Gala $2.50 |
| V Golden Delicious $1.99 |
| V Rome $2.35 |
| F Oranges |
| V Navel $2.79 |
| V Temple $2.99 |
data perm.orders (drop=type);
infile Produce;
retain Fruit;
input type $1. @;
if type='F' then input @3 Fruit $7.;
if type='V';
input @3 Variety : $16. @20 Price comma5.;
run;
-
Which SAS statement indicates
that several other statements should be executed when
Record
has a value of A?
| 1---+----10---+----20---+----30 |
| A 124153-01 |
| C $153.02 |
| D $20.00 |
| D $20.00 |
- Which is not true for the following
statements (X indicates a header record)?
if code='X' then do;
if _n_ > 1 then output;
Total=0;
input Name $ 3-20;
end;
-
What happens when the condition
Type='P' is false?
if type='P' then input @3 ID $5. @9 Address $20.;
else if type='V' then input @3 charge 6.;
-
What happens when
Last
has a value other than zero?
data perm.household (drop=code);
infile citydata end=last;
retain Address;
input type $1. @;
if code='A' then do;
if _n_ > 1 then output;
Total=0;
input Address $ 3-17;
end;
else if code='N' then total+1;
if last then output;
run;
-
Based on the values in the program
data vector, what happens next?
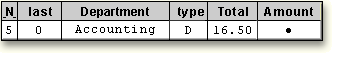
| 1---+----10---+----20---+----30 |
| D Accounting x3808 |
| S Paper Clips $2.50 |
| S Paper $4.95 |
| S Binders $9.05 |
| D Personnel x3810 |
| S Markers $8.98 |
| S Pencils $3.35 |
data work.supplies (drop=type amount);
infile orders end=last;
retain Department Extension;
input type $1. @;
if type='D' then do;
if _n_ > 1 then output;
Total=0;
input @3 Department $10. @16 Extension $5.;
end;
else if type='S' then do;
input @16 amount comma5.;
total+amount;
if last then output;
end;
run;
|